SRF to Oil
Fundraising campaign by
Francesco Saverio Guarino
-
€1.00raised of €2,500,000.00 goal goal
Executive Statement
The project consists in the construction of one industrial plant for the production of fuel oil (low sulfur content fuel) from residual plastics and SRF (Solid Recovered Fuels) materials that are otherwise destined to landfill or incineration.
The technology integrates perfectly with the separate collection o waste: only around 50% of the collected plastic can be infact recycled. The rest can not be separated into its components or is too dirty, and is actually destined to landfill or incineration. Unfortunately often it is directly disposed into the sea creating plastics polluting islands.
The problem of disposing non-recyclable plastic is extremely serious and felt all over the world.
The project consists in the construction of a first industrial plant capable of treating 7,500 tons per year. This plant will act as a demonstrator to spread the technology all over the world, contributing strongly to the solution of the residual plastic pollution problem.
The oil produced by the plant has an extremely receptive market as it replaces, at lower prices, fossil oil and other derivatives used for the production of liquid fuels, especially for vehicles.
The technology that will be used (catalytic pyrolysis), is advanced and innovative, but is extremely reliable: it is the result of a long-standing collaboration between the technological partner of the project and ENI, the leading Italian fuel extraction and refining company.
The plant is capable of processing 7,500 tons per year of material, produces about 6,000 tons per year of oil, and will be realized and commissioned with a total investment of £ 3,500,000.
The economic returns of the investment will be used to further develop the technology and to spread it wordwide. These returns will be accompanied by even more significant social and environmental returns, in terms of jobs, in terms of waste recovery that otherwise go to fill landfills or to pollute rivers and seas, and in terms of savings consumption of exhaustible materials such as fossil fuels.
The project involves the construction of a pilot project in Uk on recycling used tires, rubber and plastic waste by low-temperature pyrolysis. The final products of this technology are: fuel oil, fuel gas, carbon and metal. All these products are sufficiently in demand in Uk, especially the first two.
The purpose of this business plan is to analyze the application of this technology in Uk and the development of a pilot project.
The analysis of the situation in Uk suggests that this technology is very relevant and cost-effective for Uk. Construction of the pilot plant will at least partially solve two big problems in Uk: Dispose of waste that pollute the environment, and to provide themselves with alternative heating oil, which is extremely important now for Uk.
Created specifically for this project financial model demonstrates the economic efficiency of the project. A relatively large investment in this project, even in the worst case, fully repaid within 3 years and in the future profitability of the plant exceeds 50%. This is undoubtedly a very good result. Construction of the pilot project will not only teach the profits from his work, but also to optimize the technology to expand the resource base and on the basis of the experience gained to replicate data plants throughout Uk.
Existing technologies of recycling of used tires
Existing international and domestic experience shows that the most common methods of disposal of tires are burning to produce energy (the most popular burning them in cement kilns), pyrolysis at relatively low temperatures to produce a light distillate, solid fuel with similar properties to charcoal, and metal and obtaining rubber crumbs and the powder used to replace the natural rubber and synthetic polymers in the manufacture of building materials and mixtures thereof.
Restoration of worn tires
Restoring tires - is its overhaul in which updated or tire tread, in order to prolong the life of the tire. Recovery is environmentally friendly way in which can be increased tire life.
The share of retreaded tires in different countries varies. Thus, eg., In the US recovery is not actually play any role in Japan recovers only every tenth of a tire in Germany - one in five in the Netherlands - one in three.
Determinant for car owners of vehicles is primarily advantageous expense ratio and lifetime. However, from a technical point of view, no bus recovery can be repeated any number of times without affecting the quality and safety of operation (typically, the bus can be reduced as much as possible only twice). Each retreaded tire inevitably turns into a worn-out.
Widespread doubts about the quality and safety of retreaded tires. For example, retreaded tires approved for use for vehicles having a certain speed limit.
Burial of used tires
Worn tires legally or illegally stored on landfills mixed with other waste and landfills, designed exclusively for used tires. The number stored in the world of tires in landfills is estimated at a billion pieces. Lack alternatives tire recycling increases the number of tires stored in dumps. Against removal to the landfill of waste tires are economic, technical and environmental causes.
Due to the mixed landfill disposal of used tires extracted from the economic turnover, and therefore can not be used for further processing. This way of using the tires can be equated to the destruction of resources.
Worn tires, because of their properties is the product not in principle suitable for burial. As previously mentioned, the tires cause great harm to the environment. In addition, the shape of the tire and specific weight due to cavitation (the formation of voids) do not allow a regulated landfill compaction.
Lack of control over waste, arson, spontaneous combustion (eg., During a lightning strike) lead to the duration of the fire in landfills, which are due to good flammability (flammability) tires is difficult to extinguish. In 90 years this has led to devastating fires of tires in landfills in the United States and Canada, where only in Ontario during the month burned more than 12 million tires. Such fires due to the high level of emissions of gaseous and liquid substances lead to severe air pollution, topsoil, subsoil waters.
Recycling tires into crumb
Shredding rubber waste recognized as the most simple and rational way of processing, as it allows to preserve physical, mechanical and chemical properties of the material. However, it is the final stage of the use of the resulting chips and a stumbling block cost-effective solution to the problem of complete recycling of rubber waste.
To render the additive in paving or asphalt mastic, need to make the formulation. Two equal-sized wheels, but different manufacturers, will in their composition heterogeneous mass in which you want to add components to impart the desired properties. It is known that for over a hundred years there have been numerous efforts to combine rubber with bitumen and asphalt with a view to recycling and giving astringent properties of rubber-like materials. Were developed many technological schemes of direct introduction of rubber in asphalt mixture, the use of crumb rubber as filler in road-building materials.
Were built hundreds of experimental sections of roads, bridges and airfields coatings, which initially showed a wonderful performance. But then there was a slow swelling of the rubber particles trapped in the structure of asphalt. Coverage under such internal loads and decompresses rapidly destroyed. Unrelated rubber particles of asphalt and chip, practically unchanged, carried by the wind, contaminating the surrounding area.
Thus, more than a century of negative experience with rubber waste in road construction compromised in the eyes of experts Road the idea of using rubber (vulcanized rubber) in road construction materials.
To produce crumb of any product, you must purchase additional equipment that will bring to nothing the declared comparative cheapness. For such production requires grit with minimum dimensions that require the use of cryogenic grinding technology. In addition, the range of products that can be made from rubber crumb is limited. This coating for sports grounds, a pavement for tram and railway crossings, and so on.
Incineration of tires in cement kilns
Tyre burning occurs primarily in the cement industry and thermal power plants. Tires are used here as a material substitute coal and fuel oil. Burning tires has a large number of historical reasons. For decades, the burning of tires is an inexpensive way to produce energy. At the same time had the opportunity to save primary fuels. Alternative ways to recycle tires available in the past, often been unprofitable.
However, changing conditions, particularly in the field of environmental protection, awareness of the need for sound management of natural resources, as well as the creation of innovative technologies for recycling used tires, all this requires a new, critical approach to the method of processing.
Some disadvantages of burning tires lies in the very nature of the method. Temperature fluctuations in the combustion process leading to incomplete combustion of the tire. At temperatures below 1.100 ° C produced toxins such as chlorinated dioxin and furan. All known and undeniable fact that such processes have contributed to increasing the greenhouse effect. So, is formed in the combustion process 3,700 kg of CO2 per tonne of tires. In the production of the cement quantity used tires as fuel technologically limited. Application in the production of a large number of old tires adversely affect the quality of cement, as contained in them began to show in the cement as iron oxide, which stains the material.
Pyrolysis of scrap tires
When using the tire pyrolysis technology under the influence of heat in the absence of oxygen are separated into solid, liquid and gaseous substances. Wherein long polymer chains are converted into molecular hydrogen particle. Technology Basics concluded that shredded waste tires, and waste production and the consumption of polymeric materials (polyolefins, polystyrene, etc.) Are subjected to pyrolysis at 450-550 ° C. As a result of processing obtained by pyrolysis tire pyrolysis oil, combustible gas, carbon and steel.
Pyrolysis gas, usually (unless specific tasks) is used as fuel for a partial coating on the heat consumption of the pyrolysis process itself.
Pyrolysis resins can be used as an additive to fuel oil, or may be processed together with the crude oil or its fractions, respectively, increasing the production of end products or intermediates.
Solid carbonaceous pyrolysis residue in a tire suitable as a substitute for some of the carbon black in rubber mixtures, as well as a filler for a variety of commercial products, from Bakelite resins and mixtures ending paving.
Cause
With a large variety of technological solutions proposed by both domestic and foreign experts, the priority method of disposal of rubber waste should be technologies that provide:
- high environmental safety of the proposed process;
- extremely low energy consumption of the recycling process;
- waste-free process;
- receive output products of commercial value.
Satisfies all of the requirements of the processing technology of waste rubber tires and plastic waste by low-temperature pyrolysis without oxygen.
Production Process
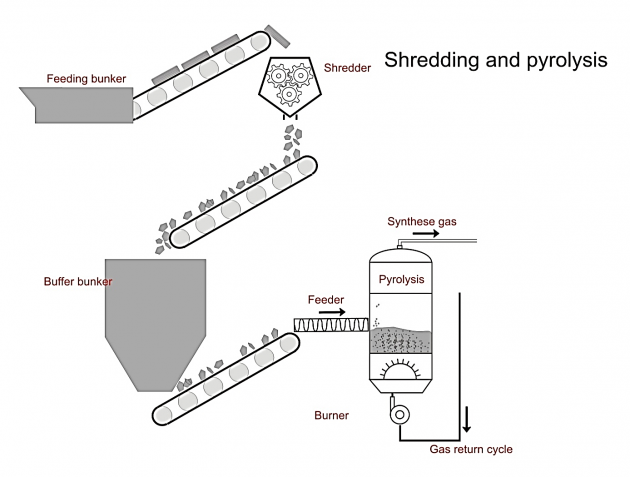
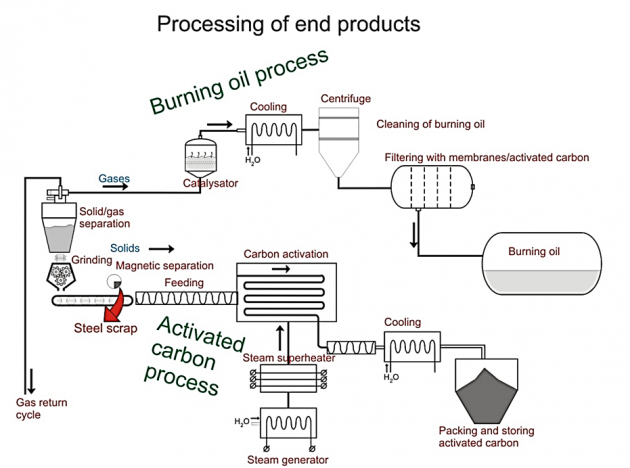
Specialist equipment is now available that utilises thermal cracking technology. Pyrolysis is a process that has been in use for 30 years, mainly for recycling tyres. The technology is proven with 15 companies engaged in some variance of the process at 87 plants throughout the world. This system has been adapted and converts plastic waste that is currently disposed of in incinerators and landfill into valuable low sulphur hydrocarbons. These systems offer the lowest cost and environmentally responsible solution for plastic waste.
The plastic waste must be cleaned and size reduced, which can be done by the existing recycling industry. After loading in the thermal ‘kettle’, the kettle is taken to a constant 360 degree heat, with
the material moved with a specially designed rolling propulsion device.
When the material is heated in the thermal kettle, the pyrolysis reaction begins, which will produce
the oil and gas.
Exhaust gas is recycled in the process of thermal cracking, in addition to the oil and gas, there will be some combustible but non-condensable gases. The gas can be directly recycled to the thermal
cracking kettle, to save fuel.
Oil and gas enter the gas separator which also separates the residual oil.
The liquid part enters the condenser to be cooled into liquid oil.
The non-liquid part enters the gas purification system, and is then burned in the cracking kettle for heating. When the pyrolysis process is finished, discharge is automatic via the auto-discharger after
the thermal kettle has cooled, ready for the new batch to begin.
The synthetic fuel that is created in the process is sealed from the atmosphere and stored in tanks, the carbon ash is ready for packaging.
With the correct recipe the synthetic fuel is pure enough to be used directly from production and will
be a high calorific value fuel oil, the quantities will exceed 75% yield.
Carbon ash can be converted into fuel pellets or recycled back into black plastics for heavy duty applications. Carbon ash is ideal for mixing with cement to make black cement or concrete, it can
also be used in road construction in asphalt.
The gas generated is stored and recycled to power the thermal kettles.
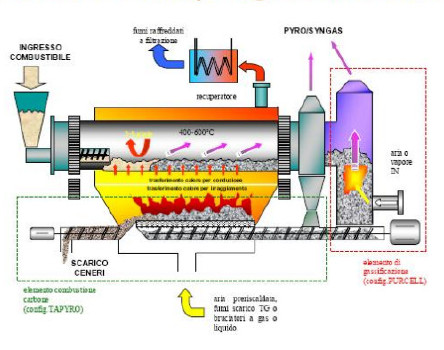
Technological scheme of installation for waste tires and waste plastic
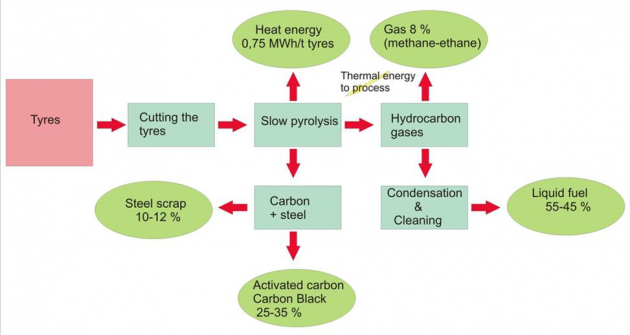
The pyrolysis process and final product
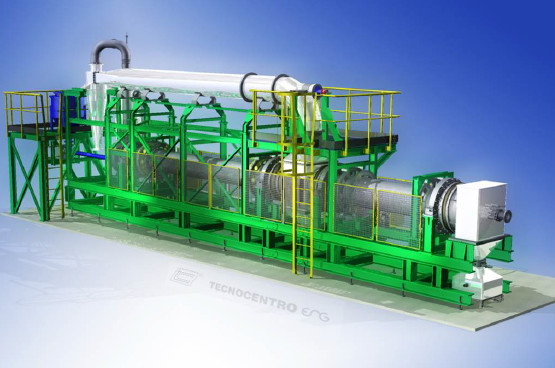
The project plants for the treatment of used tires, rubber and plastic waste with a capacity of 10,000 tons per year
Energy efficiency
The energy intensity of the pyrolysis technology is high enough. Effective process for pyrolysis of the starting material must be heated to a sufficiently high temperature and to maintain this temperature throughout the process. Then, in order to condense the vapors, they must be cooled below the condensation temperature of the liquid fraction. Evaporation and condensation of fluid require any large amount of energy as latent heat of vaporization of oil depending on the fraction of 200 to 500 kJ / kg. Therefore, at an output line for the liquid fraction of at least 1 ton per hour, the capacity of the capacitor is of the order of 200 kW. This power is dissipated as the cooling water of low temperature heat. Approximately the same amount of heat is removed with cooling of carbon black. All these low-grade heat can be recovered and used to produce electrical energy.
The costs of electricity in this technology is also quite high. The total installed capacity of electrical equipment (crushers, pumps, conveyors, and so on) is not less than 400 kW.
In the process of pyrolysis combustible gas is released. This gas with vapor of the liquid fraction fed into the boiler and burned. An exemplary flow of the gas is up to 35 kg / h. Consequently, the thermal capacity of the boiler is not less than 500 kW, and we have a surplus of thermal energy not less than 300 kW.
Convert low-grade heat into electrical energy by using ORC modules are currently commercially available. For combustion of 1 kg of gas take at least 10 m3 of air. The same quantity of combustion gases is discharged into the atmosphere at a temperature not lower than 350 ° C. These gases can be submitted at ORC module of TRI-O-GEN and get at least 300 kW of free electricity for their own needs.
The final products
During the processing of 10,000 tons per year at the output we will have at least 4,500 tons of heating oil, 3,500 tons of carbon, 1250 tons of metal courts, 750 tons of fuel gas (methane, ethane).
The main product, which is obtained by pyrolysis - a heating fuel. According to the recommendations of the developer of technology, this product can be added to motor fuel or added to crude oil to its processing at the refinery. This product is suitable to use as a backup fuel boiler installations. The calorific value of the fuel is not less than 0.01 Gcal / kg.
The second most important product of pyrolysis. Combustible gas (methane and ethane), and a pair of liquid fuel boiling fractions which were not condensed in the cooler to the boiler and completely combusted.
Carbon black, which has been obtained by pyrolysis may be used as a filler:
- in the production of new tires;
- producing paints (as a black dye);
- in the manufacture of building materials.
In addition, this product can be used as for the production of activated carbon and subsequently used as filler in exhaust filters.
Vision Statement
To create a highly profitable business that provides a solution to the huge problem of accumulating plastic waste by means of utilising already proven technology – thermal cracking – that turns the waste into hydrocarbons which can be sold on to industry and, ultimately, can be turned into new plastic with the cycle being repeated.
Business Objectives
Short term
To open site number one and so prove conclusively that the concept works both technically, practically and financially. Initial target sites are currently being assessed.
Medium term
Roll out the concept to a total of 10 sites within 7 years with production capacity at each site being either 10k or 20k tonnes.
Opportunities
Organizer
- Francesco Saverio Guarino
- Campaign Owner
- Terni, IT
No updates for this campaign just yet
Donors & Comments
- Anonymous
- Donated on Oct 19, 2020